What is the Difference Between PoE and PoE+?
Published by Cablesys on Oct 17th 2018
Network cabling systems that are PoE (Power over Ethernet) or PoE+ compliant allow electric power and data to pass over twisted pair Ethernet cabling. Understanding the differences between them can help in deciding which system to choose.
IEEE 802.3af is the original PoE standard. It specifies a maximum of 15.4W of DC power delivered to each network device. IEEE 802.3at, also known as PoE+, specifies up to 30.0W of DC power.
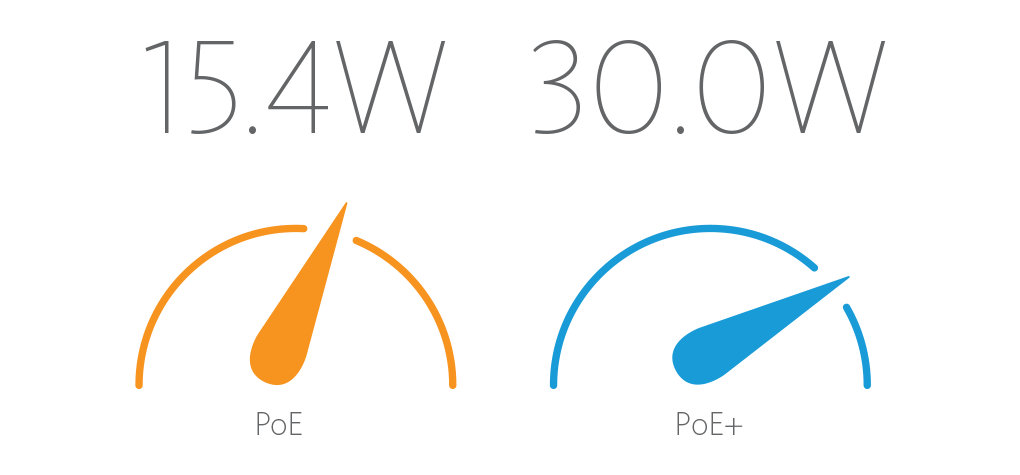
Comparison of PoE Parameters
| Property | 802.3af (802.3at Type 1) "PoE" | 802.3at Type 2 "PoE+" |
|---|---|---|
| Power available at PD | 12.95 W | 25.50 W |
| Maximum power delivered by PSE | 15.40 W | 30.0 W |
| Voltage range (at PSE) | 44.0–57.0 V | 50.0–57.0 V |
| Voltage range (at PD) | 37.0–57.0 V | 42.5–57.0 V |
| Maximum current I max | 350 mA | 600 mA |
| Maximum cable resistance per pairset | 20 Ω | 12.5 Ω |
| Power management | Three power class levels negotiated by signature | Four power class levels negotiated by signature or 0.1 W steps negotiated by LLDP |
| Derating of maximum cable ambient operating temperature | None | 5°C (9°F) with one mode (two pairs) active |
| Supported cabling | Category 3 and Category 5 | Category 5 |
| Supported modes | Mode A (endspan), Mode B (midspan) | Mode A, Mode B |
The types of devices that will be connected to the network and the amount of power they will require must be considered when evaluating a PoE solution. Below are some examples.
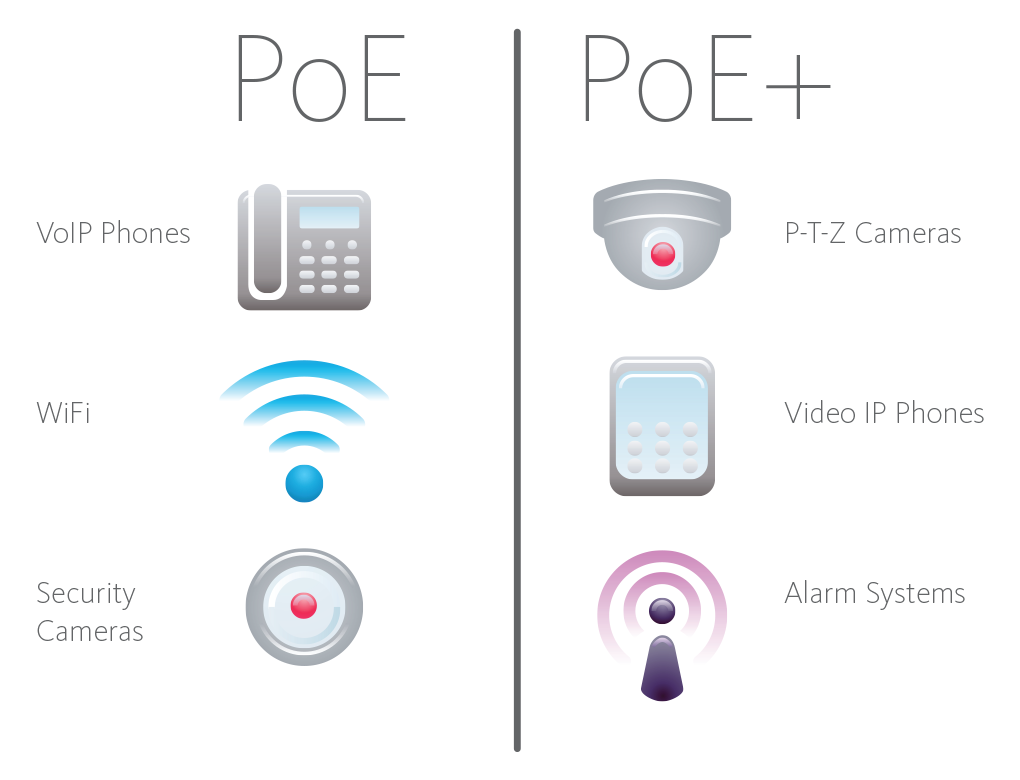
Another factor to consider is changes in technology. As more and newer devices are added to the network, higher power levels may be drawn. An existing PoE network might not be able to keep up and need to be upgraded. PoE+ will be able to support them.
Price is also a factor. Even though PoE+ cost more, there will be less worry or pain from upgrading the entire PoE system.
